In science, when we talk about evidence, we refer to scientific facts or research results.
Scientific evidence is never absolute, there are grades. Consider the weather forecast, for instance: we are usually informed on whether it will rain with a specific probability. But even that probability may have a higher or lower certainty degree.
Certainty of the evidence is how certain we are that those scientific facts are true. And, depending on the certainty of that information, we may be able to make different decisions. Thus, if the chances of rain were high, we would surely take an umbrella, whereas if they were very low, we would leave it home.
The answers to questions about treatments or healthcare interventions —such as “does aspirin prevent a heart attack?” or “does yoga improve low back pain?”— also vary in certainty, which help decision making.
Therefore, it is important to transparently assess and communicate the certainty of scientific findings. If we do not consider enough the certainty of the evidence, we could be making the wrong decisions.
The GRADE approach, widely used in health science, is the international gold standard for assessing scientific findings and communicating uncertainty in a transparent manner. This approach classifies certainty of evidence in four levels: high, moderate, low and very low.

The goal of healthcare research is to conduct more and better studies to achieve an increasing certainty. And, thus, improving decision making.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What does each grade of evidence certainty stand for?
The four grades of certainty in the GRADE approach stand for higher to lower trust in that the treatment effects observed in the studies are true. The higher the certainty is, the more confident we are that the real treatment effect is close to that estimated in the studies.
> Read pill Meaning of certainty levels (Spanish)
- How to apply the GRADE approach?
The GRADE approach is applied to the best available evidence, whether it is one single study, several studies or hundreds of them.
>Watch video Certainty depends on the type of study (English subtitles)
>Watch video Factors that modify certainty (English subtitles)
- What kind of studies can the GRADE approach be applied to?
- What overall grade of certainty have we got on treatment effects?
The evidence available for the effects of most of the treatments used today is very limited. The GRADE approach allows us to identify the grade of certainty of the treatment effects; hence, fostering informed decision making and guiding research to reduce uncertainty.
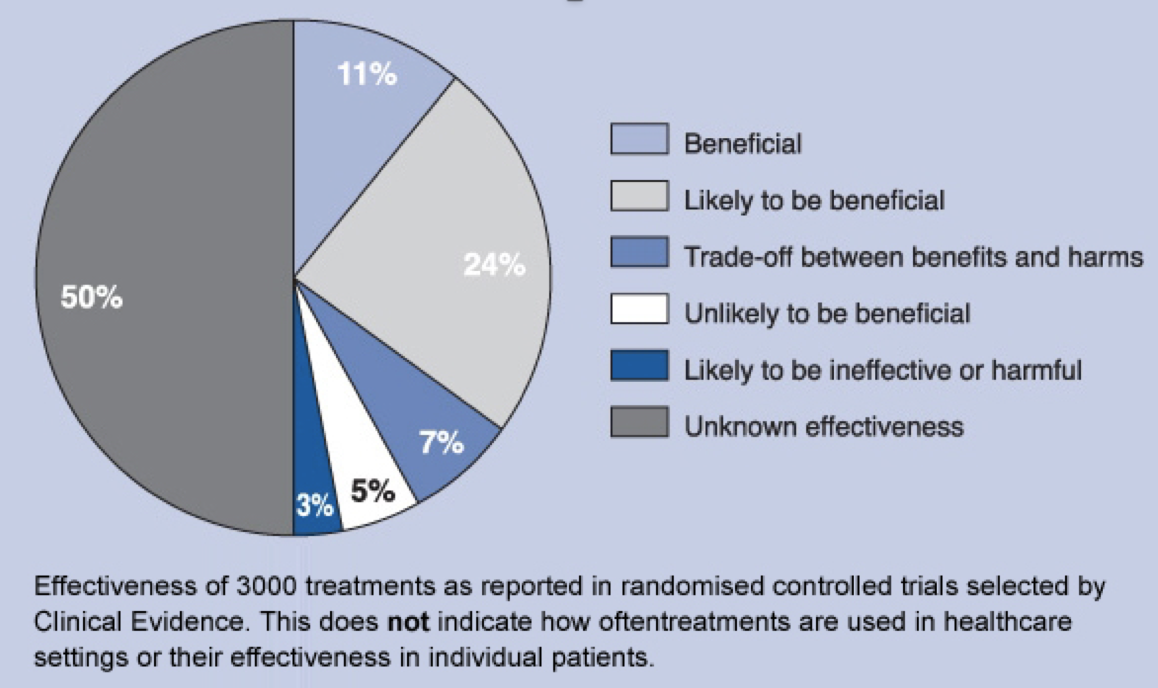
what doesn’t based on randomised controlled trial evidence? Clinical Evidence online.
http://clinicalevidence.bmj.com/x/set/static/cms/efficacy-categorisations.html
Find out more
- Schünemann HJ, Best D, Vist G, Oxman AD; GRADE Working Group. Letters, numbers, symbols and words: how to communicate grades of evidence and recommendations. CMAJ. 2003 Sep 30;169(7):677-80. Erratum in: CMAJ. 2004 Mar 30;170(7):1082.
- GRADE Handbook (Spanish version updated 2017) : Overview of the GRADE Approach.

